Understanding the roles in the Dataverse has always been complicated when it comes to implementation. Its all about how to manage the user and the levels of security in the system by using best practice and methodologies. (Don’t miss the ending).
〉〉 Security Roles in Dataverse –
- Roles – Collections of privileges assigned to a user
- Privileges – Actions that user are allowed to perform on the record or data within the environment.
- Access levels – The scope where the privileges are applied.
〉〉 What are Privileges?
It is a Specific action which user performs in Dataverse.
- Create – Allows the user to create the data or records.
- Read – Allows the user to view data or records.
- Write – Allows the user to update existing records.
- Delete – Allows the user to delete records.
- Append – Allows user to attach the related records.
- Append to – Allows the user to be attached by another record.
- Assign – Allows the user to assign record to another user.
- Share – Allows the user to share a record with another user or team
〉 〉 Access Level
- None – No Access
- User – Access to records owned by the user
- Business Unit – Access to records in the user business unit
- Parent – Child Business Unit: – Access to records in the user’s business unit and all child business unit
- Organization – Access to all the records in the organization.
〉〉The Journey of User To Security Role –
- Create Microsoft 365 User ( License) > Add user to environment > Add to Business Unit (Custom ) > Security role (Access Levels)
〉〉 Flow Chart –
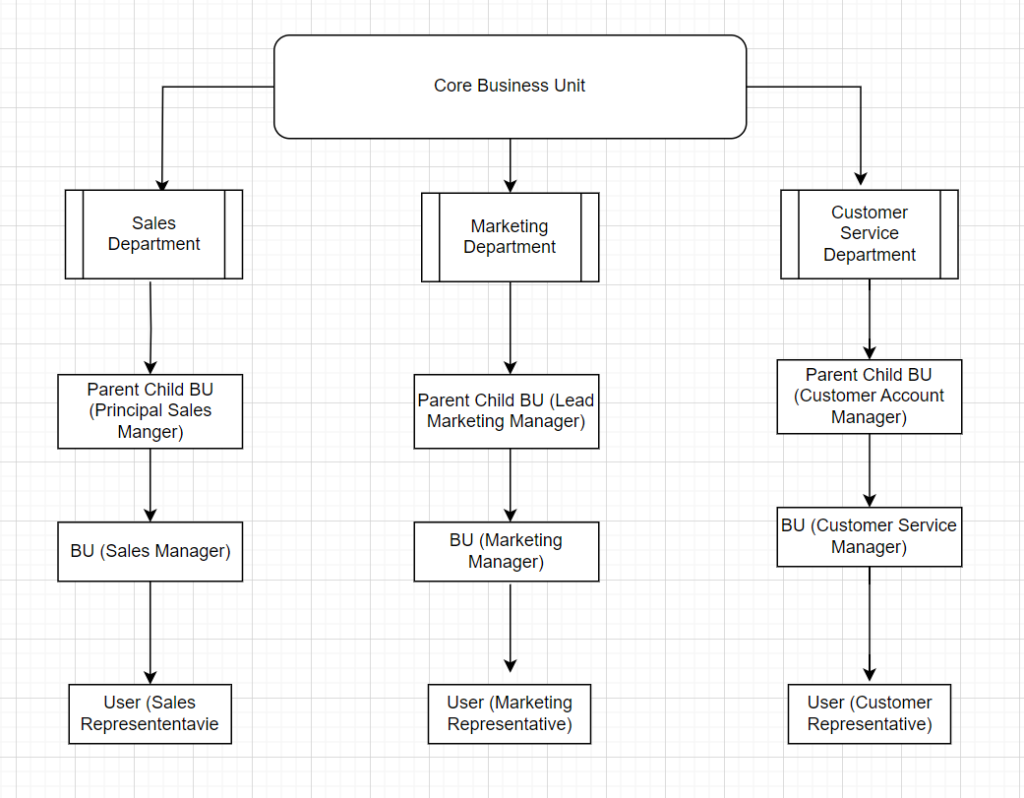
Notes by Akira28 – If the implementation is based on the high level of the data and other requirement, it can be used to define from the multiple environment level than to the basic security level process as showed above.
