The Power Platform Admin Center offers a unique and comprehensive set of tools where user can manage access on users, permissions, and security. Below are the key concepts which are available within Power Platform Admin Center.
- Users & Permissions –
- Application Users
- Business Unit
- Column Security Profiles
- Hierarchy Security Profiles
- Positions
- Security Roles
- Teams
- Users
Let just understand all this one by one.
1) Application Users
Application user is kind of non- human user which are used for running applications and integrations that will interact with the power platform. It is always used for the automation, integration and other services that needs to access the power platform environment.
Example – Suppose there is a custom integration that needs to access the data from the power platform to generate or populate report.
- First create an application user for this integration
- Navigate to the user in the Power Platform Admin Center
- Add the user and select Application User
- Fill the details and assign appropriate security roles that the integration requires, For Eg – System customizer or custom role with specific permissions.
2) Business Unit
Business Units are the organizational units within the Power Platforms environment, it helps to manage the security and data access. This unit helps to partition data and level of control access with the organizational units.
Example – If a company has 2 departments: – Sales and Service. You want to define the data that needs to be separated and only accessible to at some relevant level or limited level.
- Create 2 business unit (Sales and Service)
- Navigate to the security section
- Under the main Business Unit, click on to the New Business Unit.
- Create the Sales Business Unit and then again click on new, create Service Business Unit
- Assign users to the dedicated business unit to have control over the data based on their access units.
3) Column Security Profile
This security profiles provides control access to specific columns (fields) within the table (entity). It is very useful for protecting sensitive information that only accessible for certain users.
Example – You have a column in a table which holds a sensitive data like ” Salary”. One can follow the below steps to achieve a column level security when meeting up with such scenarios.
- Create a column security profile
- Navigate to setting section
- Go to Column security profile and click on New profile
- Name it with the profile as “Salary Viewer”
- Add the column security to “Salary” to the profile and define whether who can read, update or create data on that column.
- Assign the profile to user who can access the salary column.
4) Hierarchy Security Profile
The security profile allows an organization to configure the data according to assigned accessible roles on an organizational hierarchy, ensuring the managers and other hierarchy define can access to the data of their subordinates.
Example – For example in sales team, sales manager should be able to access and see the records to their direct subordinates.
- Create a hierarchy security profile.
- Navigate to the Settings section.
- Under “Hierarchy Security”, configure the hierarchy rules, specifying who can access whose data based on their position in the hierarchy.
- Apply this profile to the relevant business units or teams.
5) Positions
It represents the job title with an organization, that helps to understand the structured hierarchy and control access to the data based on the job positions defined.
Example – Job titles like Marketing Representative, Marketing Manager etc. All these designations help to define the job position in the system.
6) Security Roles
It is a kind of configuration which helps one to define a set of permission from various actions and data, this is like what one can access and control over the data in system.
Example – Create a security role for a Marketing representative, you can even copy other roles while creating one. If that are created previously and define there with user access privileges.
7) Teams
Teams are like a group of users who are assigned as security roles collectively, that make easier for an organization to manage permission for multiple users.
Example – You have a team working on particular task or department as a team.
8) Users
User section helps you to manage the users accounts, including the permission, roles and accessibility to the power platform environment.
Example – When you a user joins an organization need to be added and assign necessary role while adding into environment.
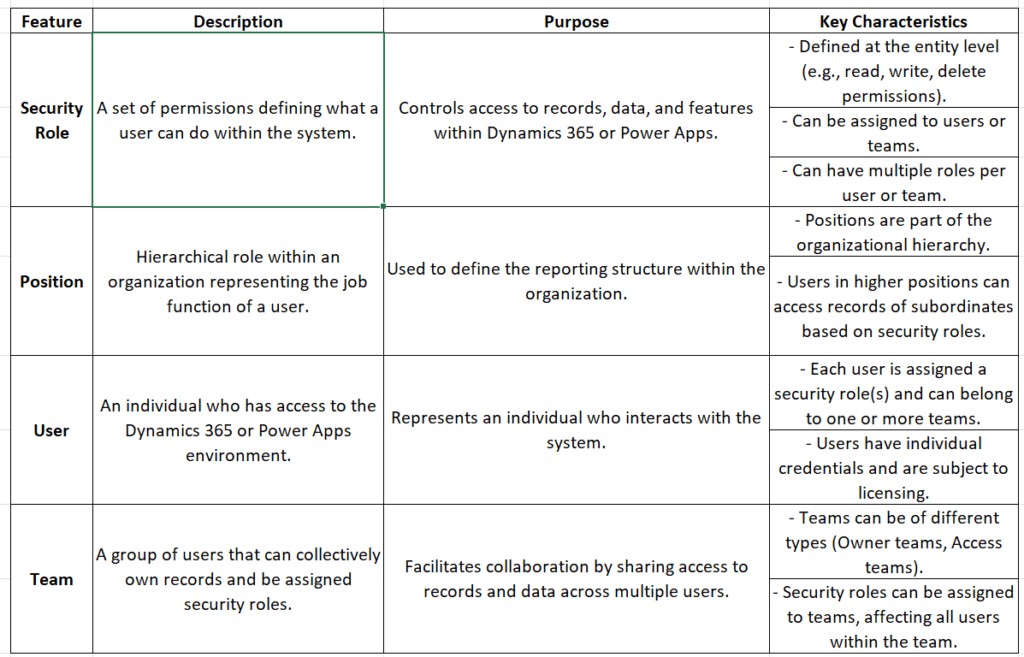
Notes by Akira 28 – Below chart will help you understand the basic difference of Security role, Position , User and Team.